Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
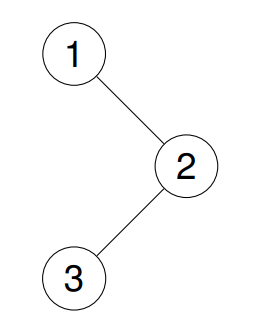
Example 1: Input: root = [1,null,2,3] Output: [1,3,2] Explanation:
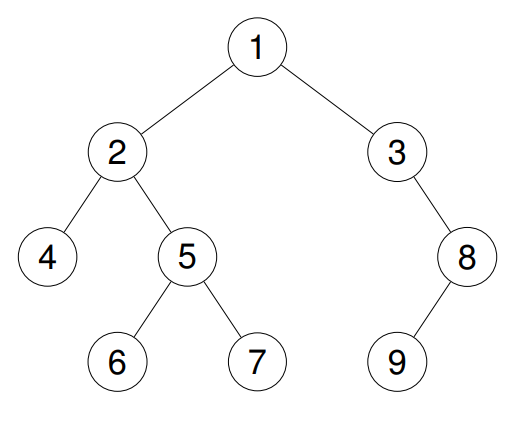
Example 2: Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9] Output: [4,2,6,5,7,1,3,9,8] Explanation:
Example 3: Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 4: Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/Recursion - O(n) time - O(n) space
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> result;
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return vector<int>();
inorderTraversal(root->left);
result.push_back(root->val);
inorderTraversal(root->right);
return result;
}
};Stack - O(n) time - O(n) space
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
TreeNode* curr = root;
while (curr != NULL || !stack.empty()) {
while (curr != NULL) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr->left;
}
curr = stack.top();
stack.pop();
res.push_back(curr->val);
curr = curr->right;
}
return res;
}
};Morris Traversal - O(n) time - O(1) space
Using a Threaded Binary Tree.
- Initialize current as root
- While current is not NULL
- If current does not have left child
- Add current’s value
- Go to the right, i.e., current = current.right
- Else
- In current’s left subtree, make current the right child of the rightmost node
- Go to this left child, i.e., current = current.left
- If current does not have left child
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
TreeNode* curr = root;
TreeNode* pre;
while (curr != nullptr) {
if (curr->left == nullptr) {
res.push_back(curr->val);
curr = curr->right; // move to next right node
} else {
pre = curr->left;
while (pre->right != nullptr && pre->right != curr) { // find rightmost
pre = pre->right;
}
if (pre->right == nullptr) {
// establish a link back to the current node
pre->right = curr;
curr = curr->left;
} else {
// restore the tree structure
pre->right = nullptr;
res.push_back(curr->val);
curr = curr->right;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};