Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Examples
Example 1: Input: root = [1,null,2,3] Output: [1,2,3] Explanation:
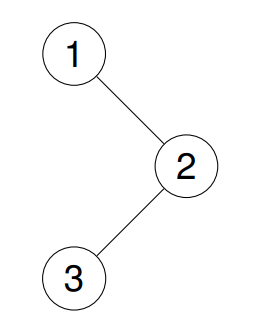
Example 2: Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9] Output: [1,2,4,5,6,7,3,8,9] Explanation:
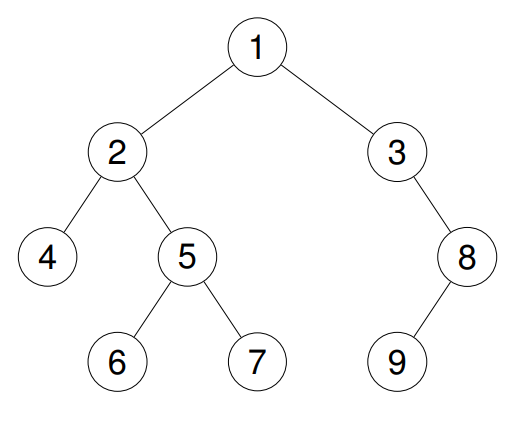
Example 3: Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 4: Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/Recursion - O(n) time - O(n) space
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> result;
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return vector<int>();
result.push_back(root -> val);
preorderTraversal(root -> left);
preorderTraversal(root -> right);
return result;
}
};class Solution {
private:
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& answer) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
answer.push_back(root->val); // visit the root
preorderTraversal(root->left, answer); // traverse left subtree
preorderTraversal(root->right, answer); // traverse right subtree
}
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> answer;
preorderTraversal(root, answer);
return answer;
}
};Stack - O(n) time - O(n) space
Let’s start from the root and then at each iteration pop the current node out of the stack and push its child nodes. In the implemented strategy we push nodes into the output list following the order Top->Bottom and Left->Right, which naturally reproduces preorder traversal.
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return vector<int>();
vector<TreeNode*> stack = {root};
vector<int> output;
while (!stack.empty()) {
root = stack.back();
stack.pop_back();
if (root != nullptr) {
output.push_back(root->val);
if (root->right != nullptr) {
stack.push_back(root->right);
}
if (root->left != nullptr) {
stack.push_back(root->left);
}
}
}
return output;
}
};Morris Traversal - O(n) time - O(n) space
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return vector<int>();
}
vector<TreeNode*> stack = {root};
vector<int> output;
while (!stack.empty()) {
root = stack.back();
stack.pop_back();
if (root != nullptr) {
output.push_back(root->val);
if (root->right != nullptr) {
stack.push_back(root->right);
}
if (root->left != nullptr) {
stack.push_back(root->left);
}
}
}
return output;
}
};