Problem
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
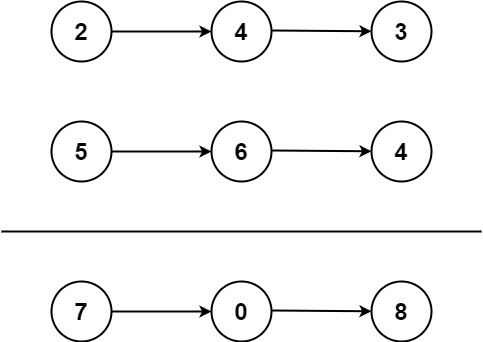
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Solution
Intuition
Iterate through two linked lists representing non-negative integers in reverse order, starting from the least significant digit. Perform digit-wise addition along with a carry value and constructs a new linked list to represent the sum. The process continues until both input lists and the carry value are exhausted. The resulting linked list represents the sum of the input numbers in the correct order.
Explanation
- Create a placeholder node called
dummyHeadwith a value of 0. This node will hold the resulting linked list. - Initialize a pointer called
tailand set it todummyHead. This pointer will keep track of the last node in the result list. - Initialize a variable called
carryto 0. This variable will store the carry value during addition. - Start a loop that continues until there are no more digits in both input lists (
l1andl2) and there is no remaining carry value. - Inside the loop:
- Check if there is a digit in the current node of
l1. If it exists, assign its value to a variable calleddigit1. Otherwise, setdigit1to 0. - Check if there is a digit in the current node of
l2. If it exists, assign its value to a variable calleddigit2. Otherwise, setdigit2to 0. - Add the current digits from
l1andl2, along with the carry value from the previous iteration, and store the sum in a variable calledsum. - Calculate the unit digit of
sumby taking the modulus (%) ofsumby 10. This digit will be placed in a new node for the result. - Update the
carryvariable by dividingsumby 10 and taking the integer division (/) part. This gives us the carry value for the next iteration. - Create a new node with the calculated digit as its value.
- Attach the new node to the
tailnode of the result list. - Move the
tailpointer to the newly added node. - Move to the next nodes in both
l1andl2, if they exist. If either list is exhausted, set the corresponding pointer tonullptr.
- Check if there is a digit in the current node of
- After the loop, obtain the actual result list by skipping the
dummyHeadnode. - Delete the
dummyHeadnode. - Return the resulting list.
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = dummyHead;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != nullptr || l2 != nullptr || carry != 0) {
int digit1 = (l1 != nullptr) ? l1->val : 0;
int digit2 = (l2 != nullptr) ? l2->val : 0;
int sum = digit1 + digit2 + carry;
int digit = sum % 10;
carry = sum / 10;
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(digit);
tail->next = newNode;
tail = tail->next;
l1 = (l1 != nullptr) ? l1->next : nullptr;
l2 = (l2 != nullptr) ? l2->next : nullptr;
}
ListNode* result = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return result;
}
};