Problem
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:

Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:

Input: head = [1,2] Output: [2,1]
Example 3: Input: head = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is the range
[0, 5000]. -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
Follow up: A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/Iterative - Stack - O(n) time - O(n) space
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
stack<ListNode*> list;
ListNode* curr = head;
while(curr) {
list.push(curr);
curr = curr->next;
}
ListNode* result = list.top();
list.pop();
ListNode* root = result;
while(!list.empty()) {
root->next = list.top();
root = root->next;
list.pop();
}
root->next = nullptr;
return result;
}
};Iterative - In-Place Reversal - O(n) time - O(1) space
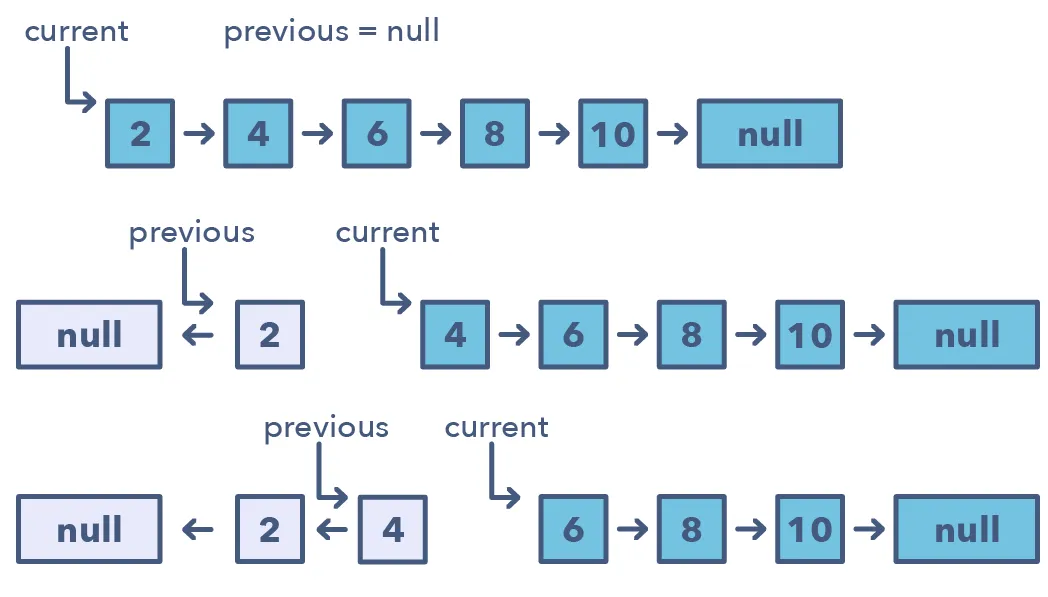
- Create a pointer
currentto point to the head of the list - Create a pointer
previousto point to the previous node processed - Iterate over list
- Save
currentto a temp variable - Reverse
currentnode by pointing itsnexttoprevious - Update
previousto thecurrentnode - Update
currentto the temp variable’snext
- Save
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
ListNode* curr = head;
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
while(curr) {
ListNode* temp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
}
return prev;
}
};Recursion - O(n) time - O(n) space
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
ListNode* h2 = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next=prev;
return h2;
}
};