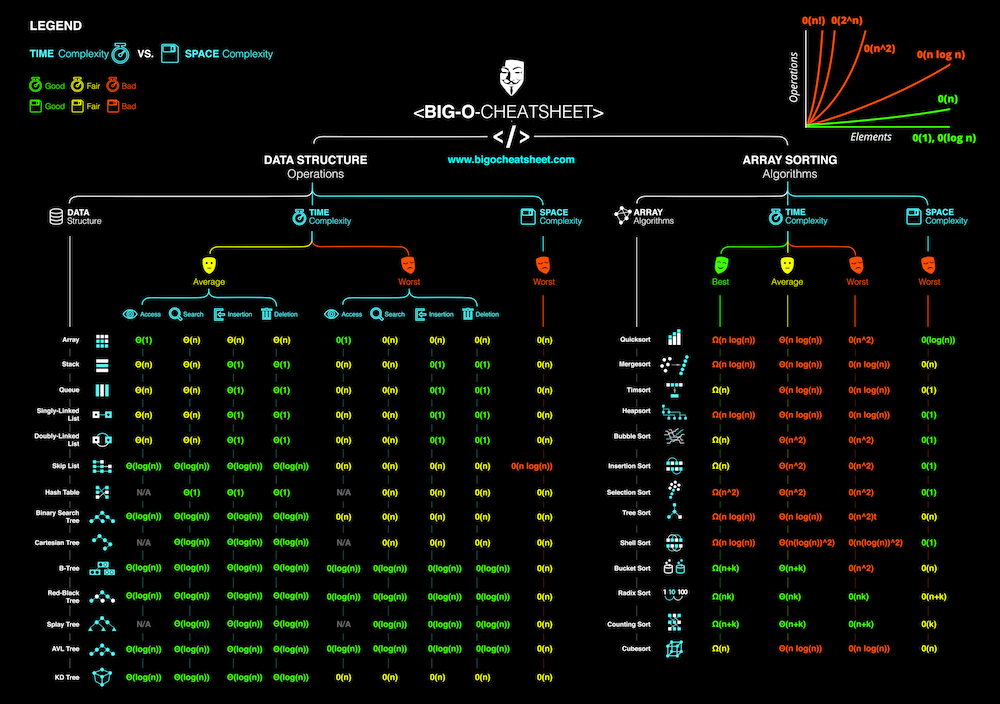
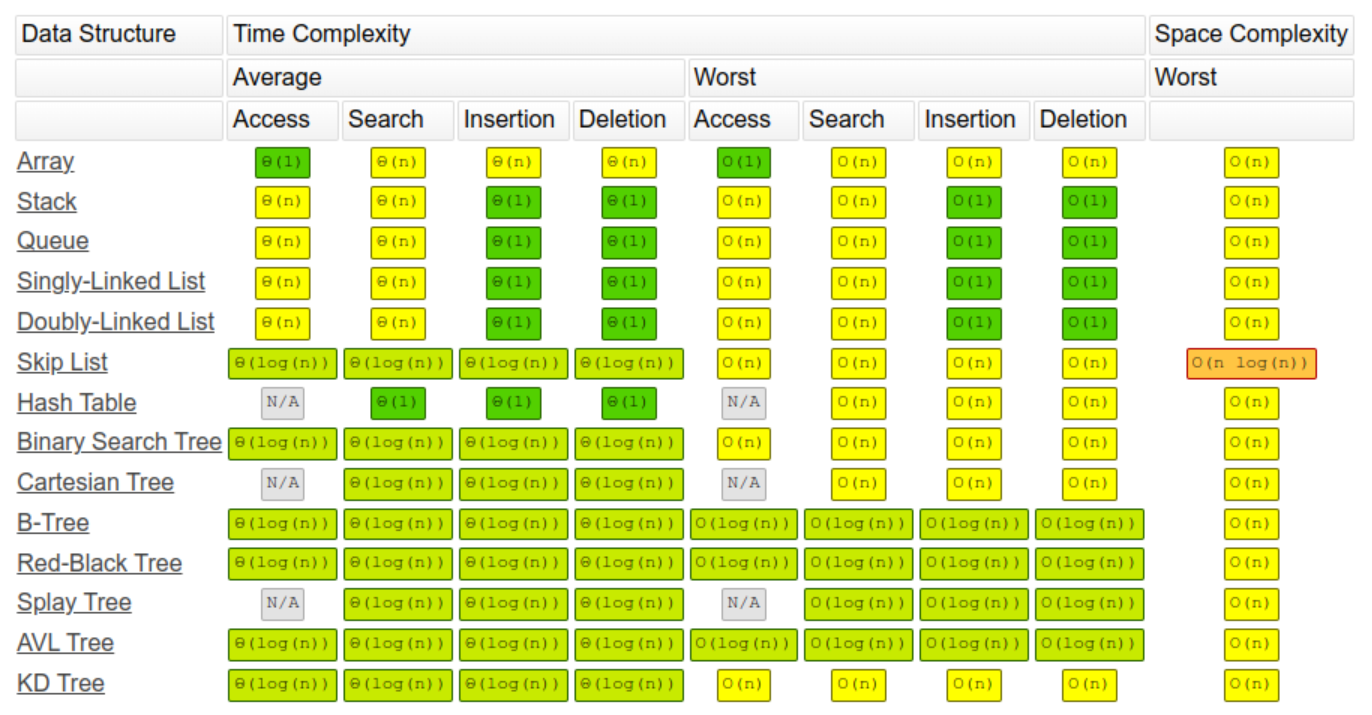
Time and space complexity expresses the rate of growth of the time and the space an algorithm takes up depending on the growth of its inputs or factors. This is expressed in Big O notation.
Big O notation describes the limiting behavior of a function as the arguments tend toward a value or infinity. i.e. it describes the growth of a function time as it relates to input growth.
This is considered worst-case complexity.
In increasing order of complexity these are:
Properties
- O(c + n) = O(n) where c is constant
- O(cn) = O(n) where c is constant
Time complexity
- Add the runtime complexity if the algorithm takes the form do x then do y
- Multiple the runtime complexities if the algorithm takes the form do y for each time you do x
Examples
Recursion
Recursion complexity is proportional to the maximum depth of the recursion tree, i.e. the length of longest path for recursion.
This is O(branches ^ depth) where
- Branches is the number of recursive calls in each iteration
- Depth is the total number of iterations
This is most often O(n) if the branches are 2 and the calls don’t go all the way to n.
For most other recursions where we make multiple calls and the calls go all the way to n, the complexity is O(n!)
Different Inputs
In a nested loop with two different inputs, the runtime won’t be O(n²), it’ll be O(a*b) where a and b are the lengths of the inputs respectively
Sorting array of strings
Suppose we had an algorithm that took in an array of strings, sorted each string, and then sorted the full array. What would the runtime be?
Initial intuition would be:
- Sorting each string is
O(n log n)and we have to do this for each string, so that’s O(n * n log n). - We also have to sort this array, so that’s an additional
O(n log n)work. - Therefore, the total runtime is
O(n^2 log n + n log n), which is0(n^2 log n).
This is incorrect. The problem is that we used n in two different ways. In one case, it’s the length of the string. And in another case, it’s the length of the array.
In an interview, you can prevent this error by not using n, or by only using it when there is no ambiguity as to what n could represent. Let’s define new terms-and use names that are logical.
- Let s be the length of the longest string.
- Let a be the length of the array.
- Sorting each string is
0( s log s). - We have to do this for every string (and there are
astrings), so that’s0( a*s log s). - Now we have to sort all the strings. There are
astrings. You should also take into account that you need to compare the strings. - Each string comparison takes
O(s)time. - There are
O(a log a)comparisons. - Therefore this will take
0( a*s log a)time. - Add up the two parts, you get
0( a* s ( log a + log s)).
Amortized time
In the case of Vector growth for example, the data structure grows in size infrequently. Even though this growth is O(n), it’s so infrequent that it can be amortized over all the access and insertion operations, essentially bringing actual time to O(1)
Space complexity
The way this is calculated is a function of the size of the data
- An array of n size takes up n space, so O(n)
- A two-dimensional array of n * n size takes up n^2 space, so O(n²)
A stack in recursive function counts for space as well